“社死”是目前人们关注和热议的问题。遭遇社会排斥是“社会性死亡 (social death) ”的一种重要表现(Steele et al, 2015)。排斥经历(Ostracism experience)是社交互动中常见的一种负面体验,指个体在社交活动中遭受他人排斥的感受。其可以分为两种主要类型:拒绝经历(Excluded experience)和忽视经历(Ignored experience)(Molden et al, 2009)。拒绝经历涉及到明确、主动和直接的排斥,即个体感知到自己不受他人欢迎;而忽视经历则涉及隐蔽、被动和间接的排斥,个体会感知到被他人忽略或遗忘。经历社会排斥可能引发报复意图等一系列心理和行为问题(Goldner et al, 2019)。深入探讨排斥经历背后的神经机制有助于更深入地认识这一现象,并为制定减缓其负面后果的神经调控措施提供方向。
已有研究提示,心理变量的不良影响具有神经基础(Goldin et al, 2009)。可以推测,排斥经历的负面结果可能也存在神经机制。报复意图常常发生在排斥经历后,指对他人实施报复的倾向或反应(Goldner et al, 2019),被视为个体对排斥经历进行情绪调节的一种策略(Yeager et al, 2011)。研究表明,排斥经历和报复意图可能存在共同的神经机制(Mwilambwe-Tshilobo and Spreng, 2021)。因此,排斥经历对报复意图的引发可能具有神经基础。
近期,西南大学心理学部夏凌翔教授课题组在《Cerebral Cortex》杂志上发表了一篇题为“Resting-state neural correlates of individual differences in ignored experience and its deleterious effect”的学术论文。该研究纳入198名大学生,所有参与者均进行了静息态功能磁共振扫描,采用量表测量了其排斥经历和报复意图得分。通过计算ALFF(Amplitudes of low-frequency fluctuations)、功能连接与排斥经历(包括拒绝经历、忽视经历)的相关,并纳入报复意图进行结构方程模型分析。结果发现:(1)忽视经历与右侧额上回(superior frontal gyrus, SFG)的自发活动呈正相关(图1a);(2)右侧SFG-左侧小脑后叶(cerebellum posterior lobe, CPL)与忽视经历正相关(图1b)、右侧SFG-双侧脑岛(insula)(图1c)和右侧SFG-双侧顶上小叶(inferior parietal lobule, IPL)(图1d)与忽视经历呈负相关;(3)右侧SFG-左侧CPL以及右侧SFG-右侧IPL的功能连接可以通过忽视经历的中介作用与报复意图相关。
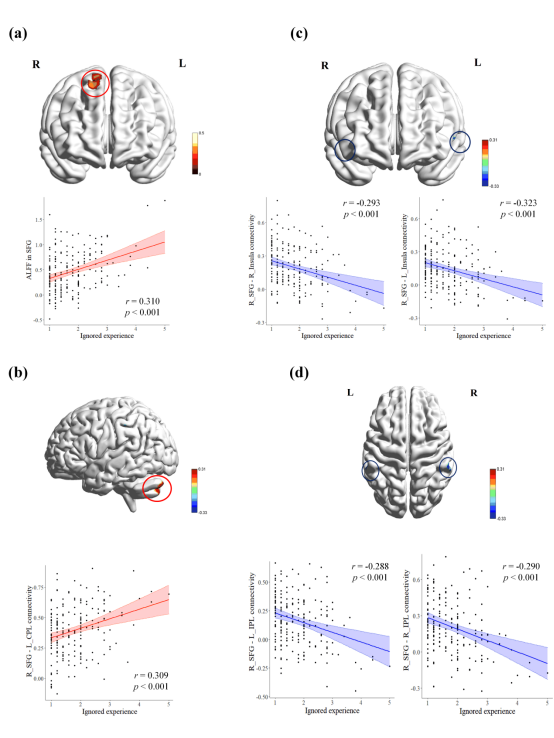
图1 控制性别、年龄、头动后的忽视经历与脑区活动/功能连接的相关
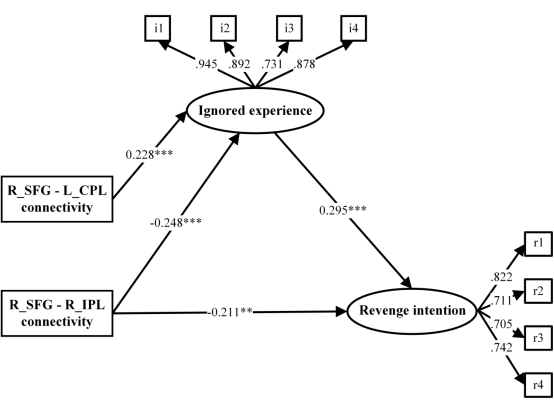
图2 功能连接、忽视经历与报复意图关系的结构方程模型
该研究的结果提示,SFG、SFG与CPL/脑岛/IPL之间的功能连接很可能是忽视经历的重要神经机制。例如,应激体验与情绪失调是忽视经历的重要心理成分。应激经历与额顶网络的活动与有关(Kim-Spoon et al, 2021),情绪失调涉及了SFG的活动(Morese et al, 2019;Ong et al, 2019)、前额叶与小脑(Rabellino et al, 2018)以及脑岛之间的异常功能连接(Fonzo et al, 2016)。
此外,报复意图可以视为是一种不良的情绪调节策略,而不良的情绪调节与SFG、IPL等脑区的活动相关(Morese et al, 2019;Sequeira et al, 2021),CPL在报复性攻击中也发挥了重要作用(Klaus and Schutter, 2021)。这提示右侧SFG-左侧CPL以及右侧SFG-右侧IPL的功能连接可能预测了个体在日常生活中对忽视的感知,并进而预测个体的报复意图。
该研究揭示了忽视经历的个体差异的脑关联,促进了对排斥经历的神经机制的理解。此外,忽视经历对报复意图的促进作用的神经基础很可能是SFG-CPL以及SFG-IPL之间的功能连接。通过揭示忽视经历和报复意图的个体差异的脑关联,可以为忽视经历和报复意图的高风险人群的的神经调控提供预防和干预思路。
该成果近期发表在《Cerebral Cortex》上,夏凌翔教授为通讯作者,博士生岑雨珊为第一作者。本研究获得国家自然科学基金(32171071)和重庆市自然科学基金(cstc2021jcyj-msxmX0607) 项目的资助。
论文索引:Cen, Y. S., Li, W., & Xia, L. X. (2023). Resting-state neural correlates of individual differences in ignored experience and its deleterious effect. Cerebral Cortex, bhad433. Advance online publication. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhad433
参考文献
Fonzo GA, Ramsawh HJ, Flagan TM, Simmons AN, Sullivan SG, Allard CB, Paulus MP, Stein MB. Early life stress and the anxious brain evidence for a neural mechanism linking childhood emotional maltreatment to anxiety in adulthood. Psychol Med. 2016:46(5) 1037–1054
Goldin PR, Manber T, Hakimi S, Canli T, Gross JJ. Neural bases of social anxiety disorder: emotional reactivity and cognitive regulation during social and physical threat. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2009:66(2):170–180
Goldner L, Lev-Wiesel R, Simon G. Revenge fantasies after experiencing traumatic events: sex differences. Front Psychol. 2019:10:886
Molden DC, Lucas GM, Gardner WL, Dean K, Knowles ML. Motivations for prevention or promotion following social exclusion: being rejected versus being ignored. J Pers Soc Psychol. 2009:96(2): 415–431
Morese R, Lamm C, Bosco FM, Valentini MC, Silani G. Social support modulates the neural correlates underlying social exclusion. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2019:14(6):633–643
Mwilambwe-Tshilobo L, Spreng RN. Social exclusion reliably engages the default network: a meta-analysis of cyberball. NeuroImage 2021:227:117666
Kim-Spoon J, Herd T, Brieant A, Peviani K, Deater-Deckard K, Lauharatanahirun N, Lee J, King-Casas B. Maltreatment and brain development: the effects of abuse and neglect on longitudinal trajectories of neural activation during risk processing and cognitive control. Dev Cogn Neurosci. 2021:48:100939
Klaus J, Schutter D. Functional topography of anger and aggression in the human cerebellum. NeuroImage. 2021:226:117582.
Will GJ, Crone EA, van Lier PA, Güroglu B. Neural correlates of retalia- ˘ tory and prosocial reactions to social exclusion: associations with chronic peer rejection. Dev Cogn Neurosci. 2016:19:288–297
Ong WY, Stohler CS, Herr DR. Role of the prefrontal cortex in pain processing. Mol Neurobiol. 2019:56(2):1137–1166
Rabellino D, Densmore M, Théberge J, Mckinnon M, Lanius R. The cerebellum after trauma: resting-state functional connectivity of the cerebellum in posttraumatic stress disorder and its dissociative subtype. Hum Brain Mapp. 2018:39(3):1–3
Sequeira SL, Silk JS, Edershile EA, Jones NP, Hanson JL, Forbes EE, Ladouceur CD. From scanners to cell phones: neural and realworld responses to social evaluation in adolescent girls. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2021:16(7):657–669.
Steele C, Kidd DC, Castano E. On social death: ostracism and the accessibility of death thoughts. Death Stud. 2015: 39(1):19-23.





